任劲松课题组周丽同学文章被 Adv. Mater. 接收,文章发表在Adv. Mater. 2014 , 26, 2424–2430上。
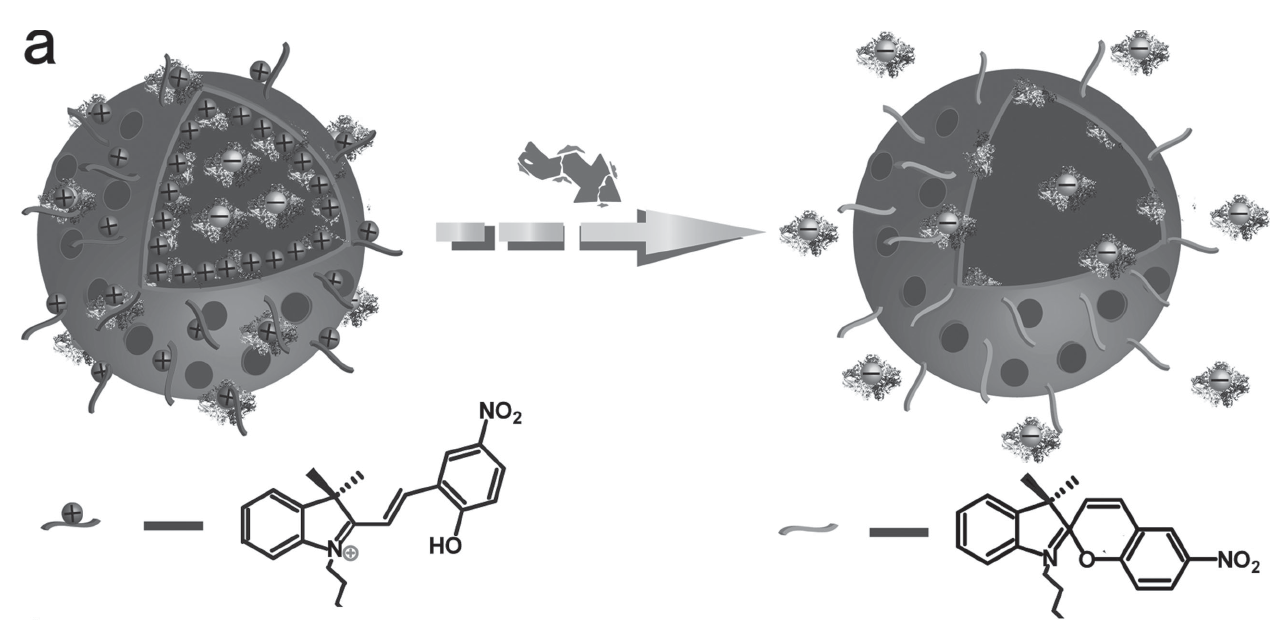
A simple DNA-mediated solvothermal method has been developed for the construction of well-defined hollow UNPs that could be used for a new paradigm to realize NIR light controlled non-invasive protein release. DNA was found to play a key role in the preparing of the hollow upconversion spheres. By coating the hollow UNPs with photo-sensitive compound, which responded to structural change of negative molecules to the neutral form upon photochemical reaction, effi cient enzyme encapsulating and sensitive NIR light triggered release were achieved. The in vitro studies further showed that the UNPs platforms were capable of the transportation of enzyme into living cells. Crucially, intracellular NIR triggered release of enzyme in a highly spatial and temporal precision was observed and the released enzyme also retained its biological activity. We envision that our novel approach and the resulting outstanding combination of properties could advance both the fi elds of UNPs and light-responsive protein conjugates, and will be highly benefi cial in future therapeutics and metabolic manipulation applications.